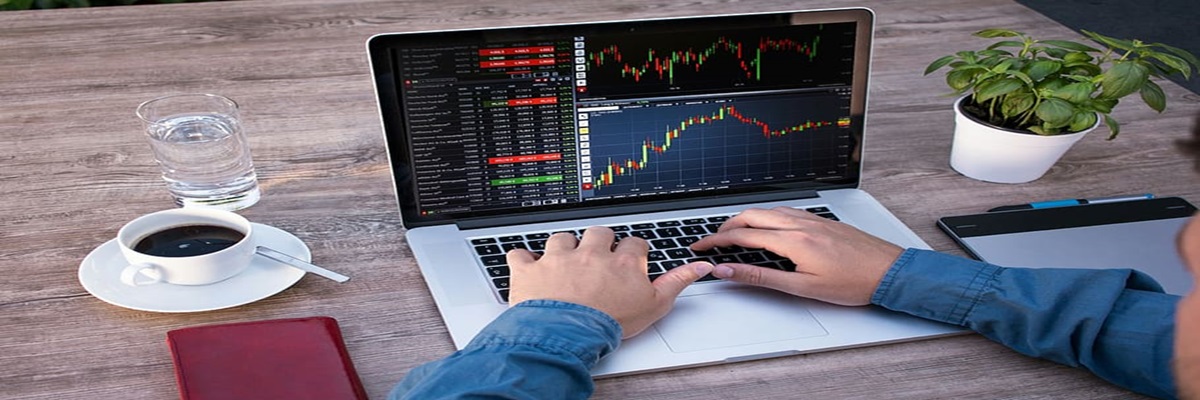
Currency Trading- Fx Futures
Forex futures are exchange-traded currency derivative contracts obligating the buyer and seller to transact at a set price and predetermined time.The price of the all futures contracts are based off the underlying asset which, in this instance, will be currency instrument.
All forex futures are written with a specific termination date, at which point delivery of the currency must occur, unless an offsetting trade is made on the initial position. Forex futures serve two primary purposes as financial instruments. First, they can be used by companies, or sole proprietors, as a hedging vehicle to remove the exchange-rate risk inherent in cross-border transactions. Second, they can be used by investors to speculate and profit from currency exchange-rate fluctuations.
The key difference between forex (SPOT FX) and forex futures is that the former is over-the-counter (OTC), meaning it’s not subject to exchange rules and regulations, while the latter, forex futures, is transacted on established exchanges, primarily the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
Forex futures are a derivative contracts that are cash settled when they expire on set dates, normally on the second business day prior to the the third Wednesday in the following contract months (March, June, Sept., Dec.).
Forex futures are traded for a number of reasons. Firstly, because of the various sizes of the contracts, they are a good tool for early investors who want to trade smaller positions, and conversely, because they are liquid, large scale investors will use them to take on significant positions.